CRMPR 26873 EQR's: 18399, 811 and 19314.:
Cardiology
Clinical Arrhythmia
Electrophysiology
Do you live far away and would like a medical opinion?
Participate in our second medical opinion program.
It's simple, fast and safe.
What is Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome?
Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) is a heart condition that occurs when there is an additional electrical pathway in the heart that can cause a fast heartbeat (tachycardia). This extra pathway can interfere with the normal heart rhythm, leading to episodes of dizziness, palpitations or even fainting. Tachycardia can occur suddenly, lasting seconds, minutes or even hours, and can be frightening and debilitating.
How does a normal heartbeat happen?
Normal heartbeats occur through a coordinated electrical and mechanical process in the heart. The heart is made up of four chambers - two atria and two ventricles - and the beat begins when an electrical signal is generated in the sinus node, located in the right atrium. The electrical signal travels through the heart muscle cells, causing the heart to contract and push blood through the body.
Normally, the heart beats regularly and at a frequency of 60 to 80 times per minute. However, in some situations, the heartbeat may become abnormal. This can occur if the electrical signal is not generated correctly or if it follows the wrong path through the heart. These abnormal beats can cause symptoms such as palpitations, dizziness and fainting, and can be a sign of more serious heart problems.
Why is the heartbeat abnormal in WPW syndrome?
WPW syndrome is a heart condition in which the heart's electrical signal takes an abnormal shortcut to spread throughout the heart. This shortcut can cause abnormal heartbeats, often rapid, leading to symptoms such as dizziness, fainting and even cardiac arrest in severe cases.
It is important to note that not all people who have the abnormal shortcut experience symptoms of WPW syndrome. Some people may just have a "WPW pattern," meaning the shortcut is present but not causing abnormal heartbeats. In these cases, these people generally do not need treatment, but it is important to have regular medical follow-up to monitor the condition.
However, in cases of WPW syndrome with abnormal heartbeats, medical treatment is necessary to control symptoms and prevent complications. Treatment may include the use of medications to regulate the heart rhythm or catheter ablation, a procedure in which the heart tissue responsible for the abnormal shortcut is destroyed with a catheter to stop the abnormal electrical signal from spreading. Proper treatment can help manage the condition and reduce the risk of serious complications.
Quals
What are the symptoms of WPW syndrome?
WPW syndrome can cause symptoms such as palpitations, dizziness and fainting. This occurs because the syndrome allows the heart's electrical signal to take an abnormal shortcut, causing the heart to beat faster than normal. Although most people with WPW syndrome do not have other heart problems, some people with WPW syndrome and other heart problems may experience more serious symptoms, such as chest pain and difficulty breathing.
In rare cases, WPW syndrome can lead to sudden death. It is important for people with WPW syndrome to monitor their symptoms and receive appropriate treatment. Treatment for WPW syndrome may include medications and procedures such as catheter ablation. It is essential that people with WPW syndrome follow their doctor's recommendations to ensure a healthy life without heart complications.
Is there a test for WPW syndrome?
Yes, there is a test to diagnose WPW syndrome, which is the electrocardiogram (ECG). The ECG measures the electrical activity of the heart and can show if there is an abnormal heart rhythm or rate. In the case of WPW syndrome, the ECG may show the presence of a delta wave, which is a characteristic sign of the disease.
In some cases, it may be necessary to perform other procedures to confirm the diagnosis or assess the need for treatment. For example, a Holter test can be used to monitor the electrical activity of the heart over an extended period of time, usually 24 hours. Additionally, an electrophysiological study can be performed to map the electrical activity of the heart and identify the exact location of the extra pathway.
How is WPW syndrome treated?
Treatment of WPW syndrome depends on the severity of symptoms, the frequency and duration of tachycardia episodes, as well as other heart conditions that may be present. In many cases, patients do not need treatment, especially if they have no symptoms.
For those with symptoms, treatment may include antiarrhythmic and heart rate-slowing medications.
Another treatment option is catheter ablation, a minimally invasive procedure in which a catheter is inserted into a vein and guided to the heart. The catheter is used to destroy the part of the heart tissue that is causing the abnormal heartbeat. This procedure is generally successful and has low complication rates.
In rare cases, when WPW syndrome is associated with other serious heart conditions, heart surgery may be necessary. It is important to highlight that WPW syndrome is a treatable condition and that appropriate treatment can significantly reduce symptoms and improve patients' quality of life.
What treatments can stop an episode of tachycardia?
There are several treatment options available to control episodes of tachycardia in people with WPW syndrome. Some of the options include:
Vagal maneuvers: maneuvers that people can perform include: coughing repeatedly, drinking cold water and the "Valsalva" maneuver. These maneuvers stimulate the vagus nerve, which helps slow the heart rate.
Medications: There are several medications that can help control tachycardia episodes in people with WPW syndrome. These medications can be administered orally or injected, depending on the severity of the episode.
Cardioversion: During cardioversion, the doctor gives an electrical shock to the heart to stop the rapid heartbeat. This allows the heart to beat normally again.
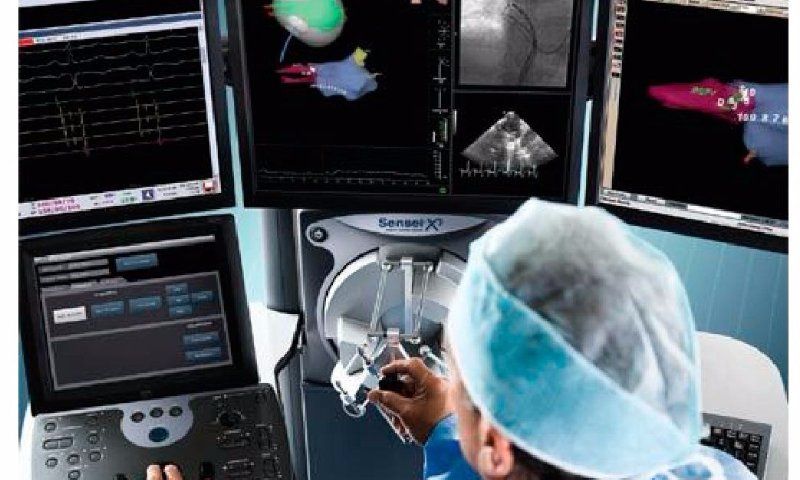
Catheter ablation: Ablation is a minimally invasive procedure that uses catheters to destroy the heart tissue that is causing the extra path in the heart. This procedure can be performed in more severe cases of WPW syndrome or in people who do not respond to other treatments.
The treatment chosen will depend on the severity and frequency of tachycardia episodes, as well as other medical factors and personal preferences. It is important to consult a doctor specializing in cardiology to determine the best treatment for each individual case.
What treatments can prevent future episodes of tachycardia?
There are treatments that can prevent future episodes of tachycardia in patients with WPW syndrome. One of these treatments is called radiofrequency ablation, which is a minimally invasive procedure performed by a specialized cardiologist. During radiofrequency ablation, a probe is inserted through a catheter and guided into the heart. The objective is to destroy the cardiac tissue responsible for the shortcut that causes tachycardia episodes. This procedure can be curative, that is, it can eliminate WPW syndrome completely.
In addition to radiofrequency ablation, there are medications that can be used to control tachycardia episodes in patients with WPW syndrome. However, these medications do not cure the disease and are not recommended to prevent future episodes of tachycardia. They are an alternative for patients who do not wish to undergo the ablation procedure or for those who are not candidates for radiofrequency ablation.
In Maringá, Dr. Marcio Gianotto is a cardiologist, arrhythmologist and electrophysiologist who performs ablation procedures to treat WPW. With more than 1,000 procedures performed in the city, Dr. Gianotto is considered one of the most experienced professionals in the region in the area of radiofrequency ablation.
If you are suffering from WPW symptoms, radiofrequency ablation may be an effective and safe solution for you. Don't hesitate to reach out to Dr. Marcio Gianotto for more information about this revolutionary procedure and how it can help you get rid of your symptoms for good.

Do you know what Vasovagal Syncope or Fainting is?
Have you ever heard of arrhythmia ablation?
Ablation for Atrial Fibrillation and Other Complex Arrhythmias.
Complex ablations for the treatment of arrhythmias such as Atrial Fibrillation and cicatricial Ventricular Tachycardia are being carried out in Maringá with the help of new equipment, previously only available in large medical centers in São Paulo and other capitals.
Click for information
Doctor Qualified by SOBRAC.