CRMPR 26873 EQR's: 18399, 811 and 19314.:
Cardiology
Clinical Arrhythmia
Electrophysiology
Do you live far away and would like a medical opinion?
Participate in our second medical opinion program.
It's simple, fast and safe.
What is Atrial Fibrillation?
Atrial fibrillation, also known as "AF", is the most common heart rhythm disorder. This condition significantly increases the risk of stroke, heart attack and other serious complications. When a person has AF, the electrical signals that control the heartbeat become abnormal. This causes a decrease in the effectiveness of the two upper chambers of the heart (the atria), which no longer pump blood properly. As a result, a small amount of blood can accumulate in these atria, forming clots that can migrate to the brain and cause a stroke.
AF can occur continuously, being called persistent or permanent, or it can be intermittent, being called paroxysmal. If you have had one or more episodes of AF but now have a normal heart rhythm, it is important to ask your doctor what to do to keep it under control. Some measures can reduce your chances of new episodes of AF, such as controlling blood pressure, avoiding excessive alcohol consumption (limit 1 to 2 drinks per day), reducing caffeine intake, treating possible thyroid problems and exercising regularly. .
What are the symptoms of AF?
Atrial fibrillation, a common heart condition, can present with a variety of symptoms but can also occur asymptomatically. When symptoms are present, people with AF may feel as if their heart is racing, skipping beats, or beating out of sync. These symptoms may be accompanied by slight tightness or pain in the chest, dizziness and difficulty breathing, especially during exercise.
In addition to these symptoms, some people may also experience fatigue, weakness, or even fainting. The feeling of shortness of breath or excessive tiredness may indicate that the heart is not pumping enough blood to meet the body's needs. Fainting can occur when the lack of oxygen to the brain is temporary, but still worrying.
If you experience any of these symptoms or have any suspicion that you may have atrial fibrillation, it is important to see a doctor immediately. AF can significantly increase your risk of serious complications, such as stroke and heart attack. Appropriate treatment can help reduce this risk, as well as symptoms and improve quality of life.
Is there a test for FA?
In addition to the electrocardiogram (ECG), there are other testing options that can help diagnose atrial fibrillation (AF). These include Holter cardiac monitoring and event monitoring.
Holter heart monitoring is a test that involves using a portable device that records the heart's electrical activity continuously for 24 to 48 hours or longer. This can help identify intermittent episodes of AF that would not be detected by a short-term ECG.
Event monitoring is a test that involves the use of a portable device that records the electrical activity of the heart only when symptoms occur. This device is usually used for a longer period of time than a Holter, such as two weeks to a month, and can help diagnose intermittent AF.
In addition to these tests, your doctor may also recommend other tests to evaluate your heart health, such as an echocardiogram. It is important to remember that early diagnosis of AF is essential to prevent serious complications, so if you suspect you may have the condition, it is important to see a doctor for evaluation and guidance.
How is AF treated?
There are several treatment options available for atrial fibrillation (AF), and the type of treatment chosen will depend on the severity and duration of the condition, as well as other individual health factors.
Medications are often used to control heart speed or rhythm in people with AF. Medicines that control heart rate help to slow the heart rate and improve blood circulation. Medicines that control heart rhythm, known as "antiarrhythmics", help maintain a normal and regular heart rhythm. Anticoagulant medications are also used to prevent blood clots from forming, reducing the risk of strokes and other complications.
In some cases, cardioversion may be performed to restore normal heart rhythm. This treatment involves applying an electrical current to the heart, under sedation, to stop AF and restore the heart's normal rhythm.
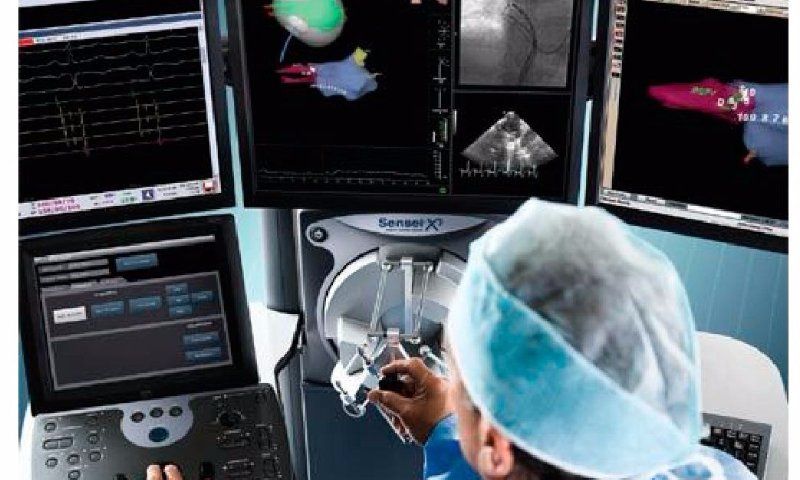
Another treatment option is ablation, which can be performed using heat energy (radiofrequency ablation) or cold energy (cryoablation) to destroy small areas of the heart that are causing the abnormal electrical signals responsible for AF. This procedure is performed through a catheter inserted through a vein in the leg and guided to the heart.
In more severe or advanced cases of AF, a device called a pacemaker may be implanted in the body. This device is capable of sending electrical signals to the heart to control the heart rhythm and keep the heart functioning properly.
It is important to remember that AF treatment must be individualized and discussed with a specialist doctor, who can assess the clinical picture and recommend the most appropriate treatment for each patient. Furthermore, adopting a healthy lifestyle, with a balanced diet, regular physical activity and controlling risk factors, such as high blood pressure and diabetes, can also help prevent the occurrence and progression of AF.
What will my quality of life be like?
Many people with AF are able to live normal lives. Still, it's important that you take the medications your doctor prescribes each day. By taking your medications correctly, you can help reduce the chances that your arrhythmia will cause a stroke.
Additionally, some people with AF may have symptoms that affect their quality of life. These symptoms can include fatigue, shortness of breath and dizziness. If you are experiencing symptoms that affect your ability to carry out your daily activities, it is important that you talk to your doctor. They can help you find ways to manage your symptoms.
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle can also help improve your quality of life with AF. This may include getting regular exercise, eating a healthy and balanced diet, reducing alcohol consumption and stopping smoking. Additionally, it is important that you keep an eye out for warning signs of a possible stroke, such as weakness or numbness on one side of the body, difficulty speaking or blurred vision.
Although having AF can be challenging, many people with the condition lead active, healthy lives. With proper treatment and a healthy lifestyle, you can help manage your condition and improve your quality of life.
Why do I need medicines?
If you have been diagnosed with atrial fibrillation, medication may be necessary to help prevent serious complications such as stroke and heart failure. Medications can help control the speed and rhythm of your heartbeat as well as prevent blood clots from forming.
The medications you will need to take depend on the type and severity of your AF. Some people may need to take medication to control their heart rate, while others only need medication to control the speed of their heartbeat. Blood thinners may also be prescribed to help prevent the formation of blood clots that can lead to a stroke.
It's important to remember that although medications can help control atrial fibrillation, they do not cure the condition. You will still need to monitor your condition regularly with medical tests and follow your doctor's recommendations to help keep your heart health in good shape.
QWhat are the medications?What might I need?
There are three main types of medications used to treat atrial fibrillation:
- Heart rate control medications: These medications include beta blockers such as metoprolol (brand name: Selozok) and carvedilol (brand name: Ictus). They work to reduce the heart rate.
- Heart rhythm control medications: These medications include amiodarone (brand name: Ancoron) and propafenone (brand name: Ritmonorm). They help restore the heart's normal rhythm.
- Anticoagulant medications: These medications help prevent blood clots from forming. The oldest and most commonly used blood thinner is warfarin (brand name: Coumadin or Marevan). If you take warfarin, you need to have regular blood tests to monitor the effects of the medication on your body. However, there are four new anticoagulant medications – dabigatran (brand name: Pradaxa), apixaban (brand name: Eliquis), rivaroxaban (brand name: Xarelto) and edoxaban (brand name: Savaysa, Lixiana) – that do not require regular blood tests and are equally effective. .
Sometimes it may be necessary to try several different medications to find what works best for you. If you experience unpleasant side effects or have difficulty paying for medications, talk to your doctor. There are ways to deal with these problems and the first step is always to inform your doctor.
In Maringá, Dr. Marcio Gianotto is a cardiologist, arrhythmologist and electrophysiologist who treats Atrial Fibrillation and performs ablation procedures to treat Atrial Fibrillation. With more than 1,000 procedures performed in the city, Dr. Gianotto is considered one of the most experienced professionals in the region in the area of radiofrequency ablation.
If you are suffering from AF symptoms, radiofrequency ablation may be an effective and safe solution for you. Don't hesitate to reach out to Dr. Marcio Gianotto for more information about this revolutionary procedure and how it can help you.

Have you ever heard of arrhythmia ablation?
Ablation for Atrial Fibrillation and Other Complex Arrhythmias.
Complex ablations for the treatment of arrhythmias such as Atrial Fibrillation and cicatricial Ventricular Tachycardia are being carried out in Maringá with the help of new equipment, previously only available in large medical centers in São Paulo and other capitals.
Click for information
8 Frequently Asked Questions About Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome (WPW).
Disease that can cause rapid heartbeats (tachycardia), eventually leading to episodes of dizziness or fainting.
Click for information
Do you know what Vasovagal Syncope or Fainting is?
Doctor Qualified by SOBRAC.